Two Force Members
A two force member is a body that has forces (and only forces, no moments) acting on it in only two locations. Two force members are an important aspect of the analysis of engineering structures in that there are the key element separating trusses (which consist entirely of two force members) from frames and machines (which have non-two force members). Even in the analysis of frames and machines, the identification of two force members will still be a necessary step in solving those problems.
In order to have a two force member in static equilibrium, the net force at each location must be equal, opposite, and collinear. This will result in all two force members being in either simple tension or simple compression as shown in the diagram below.
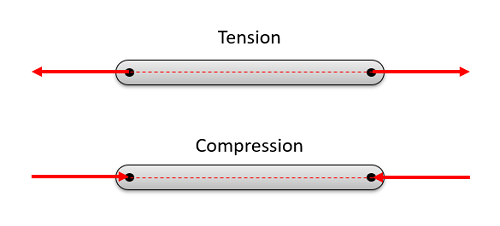
Why the Forces Must Be Equal, Opposite, and Collinear:
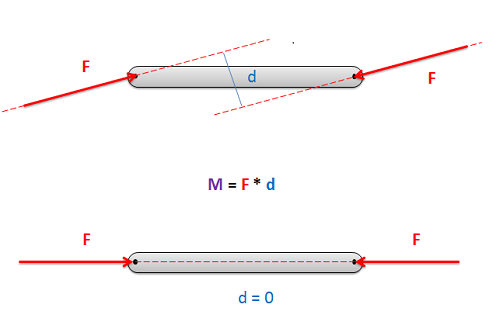
Imagine a beam where forces are only exerted at each end of the beam (a two force member). The body has some non-zero force acting at one end of the beam, which we can draw as a force vector. If this body is in equilibrium, then we know two things: 1) the sum of the forces must be equal to zero, and 2) the sum of the moments must be equal to zero.
In order to have the sum of the forces equal to zero, the force vector on the other side of the beam must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. This is the only way to ensure that the sum of the forces is equal to zero with only two forces.
In order to have the sum of the moments equal to zero, the forces must be collinear. If the forces were not collinear, then the two equal and opposite forces would form a couple. This couple would exert a moment on the beam when there are no other moments to counteract the couple. Because the moment exerted by the two forces must be equal to zero, the perpendicular distance between the forces (d) must be equal to zero. The only way to achieve this is to have the forces be collinear, and for those forces to act along the line connecting to two points where the forces are applied.
Why are Two Force Members Important:
By identifying two force members, we greatly reduce the number of unknowns in our problem. In two force members we know that the forces must act along the line between the two connection points on the body. This means that the direction of the force vectors is known on either side of the body. Additionally, we know the forces are equal and opposite, so if we determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on one side of the body, we automatically know the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the other side of the body.
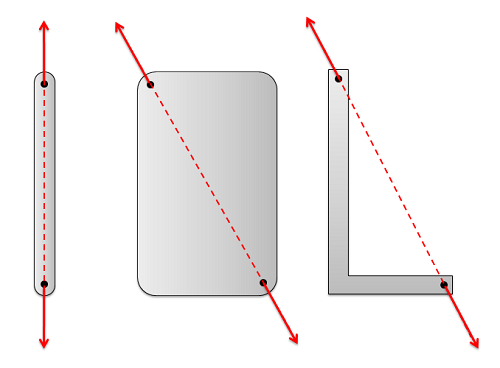
Two force members are also important in distinguishing between trusses, and frames and machines. When we analyze trusses using either the method of joints or the method of sections, we will assume everything is a two force member. If this assumption is incorrect, this will cause serious problems in the analysis. By making this assumption though, we can use some shortcuts that will make truss analysis easier and faster than the analysis of frames and machines.